Currently, most of the aerators are AC induction motor (asynchronous motor) aerators with gearbox (reduction gear).
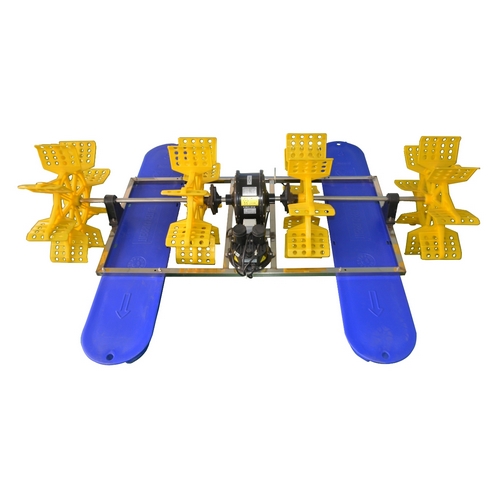

In China, the proportion of BLDC motor aerators used in aquaculture is increasing year by year, while the proportion of the market with gearbox aerator is decreasing year by year, this article will analyze the difference between the two kinds of aerators. This article will analyze the differences between the two types of aerators for your reference.

Different structure:
induction motor AC induction motor structure:
asynchronous motor asynchronous motor is divided into squirrel cage type three-phase asynchronous motor and wire wound three-phase asynchronous motor. Stator by the base, stator core, stator winding; rotor by the rotor core, rotor winding (or squirrel cage), as well as the corresponding shaft and bearings are composed. The base of the three-phase asynchronous motor has a heat dissipation rib, which increases the heat dissipation function of the asynchronous motor. The shaft of the three-phase asynchronous motor is equipped with a fan to help dissipate the heat.

Permanent magnet synchronous motor structure:
The vast majority of high-speed permanent magnet synchronous motors use a built-in rotor structure, the permanent magnets are located in the core between the squirrel cage guide bars and the rotor shaft; the squirrel cage guide bar structure provides the same principle as an asynchronous motor to start the motor, there is no can't be started, unless by other starting methods.
A permanent magnet synchronous motor consists of a stator, rotor, and end cover components. The stator is basically the same as an ordinary induction motor, with a laminated structure to minimize iron consumption during motor operation. The rotor can be made solid or laminated.

Different working principle
AC induction motor working principle:
An asynchronous motor is the stator inputs alternating current (utility 50Hz/60Hz), generating a rotating magnetic field, while the rotor is induced to produce a magnetic field so that the two magnetic fields so that rotor follow the rotating magnetic field of the stator and rotate. The rotor is slower than the stator rotating magnetic field, there is a rotational difference, not a synchronized so-called asynchronous motor. The speed difference of the asynchronous motor follows the change in load size.
Principle of operation of BLDC motor:
Synchronous motor rotor in the iron core surface affixed with pairs of magnets or iron core inserted into pairs of magnets to form an unchanging magnetic field, so that the rotor will follow the stator rotating magnetic field - up to the turn and synchronization, began to be called synchronous motor. Synchronous motor regardless of the load size, as long as not out of step, the speed will not change; the speed of the motor is determined by the frequency of the input current and the number of magnetic poles of the motor.

is an alternating current (AC) that is converted to direct current (DC) and then converted to the frequency of the required speed.
Why does an asynchronous motor aerator need a gearbox reducer?
The speed of a three-phase asynchronous motor is fixed, usually around 1500 rpm for a 4-pole motor (or 2800 rpm for a 2-pole motor). The impeller speed of an asynchronous motor oxygenator is 110 rpm. If you need to change the speed, you need to use a reducer. gearbox reducer is a mechanical transmission device that converts the high-speed rotational power of the input shaft to the low-speed rotational power of the output shaft to decelerate and increase the force. A reducer usually consists of gears, bearings, oil seals, and other components. During the deceleration of the motor through the gearbox, electrical energy is lost by about (10-20%) (depending on the newness and quality of the aerator), and the efficiency of an asynchronous motor is about 80-70%, depending on the quality.

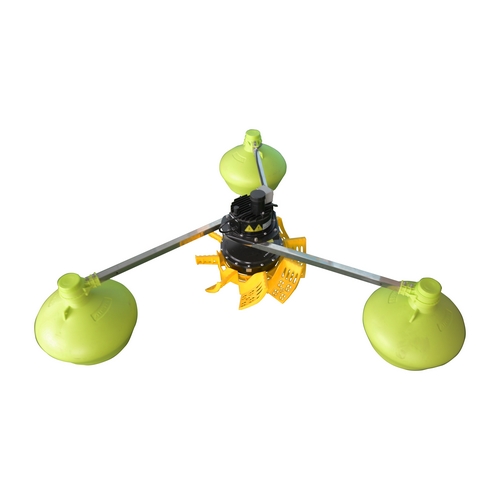
Why does a BLDC motor aerator not need a gearbox?
The magnetic field created by the fixed permanent magnets in a DC motor (brush motor) does not move but is rotated by the magnetic field created inside the coil (rotor) by the brush control coil in the sequence of energization and de-energization. The number of rotations is changed by changing the voltage. BLDC motors are based on DC motors, and instead of mechanical brushes, inverters (controllers) are used to energize the stator coils at a programmed frequency to form a rotating magnetic field that rotates the rotor of the magnets. By controlling the direction and size of the current to the coil to control the rotation of the rotor.
BLDC motors use permanent magnets as the rotor. Since there is no need to energize the rotor, brushes, and commutator are not required. Electricity to the coil is controlled externally.
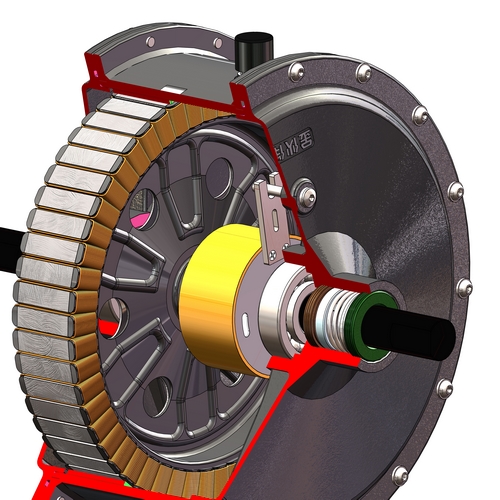
Rotor Differences:
The main structural difference between a permanent magnet synchronous motor and an induction asynchronous motor is the rotor. The asynchronous motor rotor has no permanent magnets, only the excitation winding (or squirrel cage).
A synchronous motor rotor has no excitation winding but only permanent magnets.
Why does a Brushless DC Inverter aerator save power?
Since the magnetic field of the BLDC aerator motor is generated by NdFeB (a type of permanent magnet), it is possible to avoid generating the magnetic field through the excitation current, which leads to copper consumption (resistance heating), and the copper consumption is low and the efficiency is high.
Because BLDC motor rotor operation does not need excitation current, reduces the temperature rise of the motor, the same load, permanent magnet synchronous motor temperature rise is low, low energy consumption, to achieve the purpose of power saving and energy saving.
Permanent magnet synchronous motor power density and torque density are high, compared with the asynchronous motor under the same power and torque, lightweight, and small size.

Asynchronous motor oxygenator advantages and disadvantages:
Asynchronous motor advantages:
Disadvantages:
Complicated installation, if the motor and gearbox are installed incorrectly, it will greatly shorten the service life of the machine.
Machine oil leakage will cause pond pollution. Fish and shrimp death.
As the birth rate decreases and labor costs increase, the cost of maintaining the machine will continue to rise
Inverter aerator advantages and disadvantages
Pros:
Gearbox type aerator, BLDC paddlewheel motor inverter aerator has a higher efficiency of 90-93% (high-speed motor), and the permanent magnet synchronous motor can run at low speed and high torque (compared to the high-speed motor, the efficiency will be reduced), it can directly drive the load without a gearbox. Power consumption is 70% of the asynchronous motor, about 30% power savings.
The speed of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is adjusted by the controller according to the program, and the speed starts slowly after the aerator starts, which doesn't hurt the body of the fish and shrimp.
Extremely low noise
No oil, (no need to gearbox deceleration torque increase)
The machine is light and easy to carry.
Wide range of voltage operation, for example, 380V AC, the oxygenator can run at 260V-450V.
No burning of the motor during phase failure.
Easy to install
Disadvantage:
BLDC motor permanent magnet is made of rare earth material, expensive cost.
Difficult to repair
